| Pipe Support Systems |
|
| |
|
Pipe Supports and Restraints
• Supports
– Absorb system weight
– Reduce:
+ longitudinal pipe stress
+pipe sag
+ end point reaction loads
• Restraints
–
Control or direct thermal movement due to:
+ thermal expansion
+ imposed loads |
 |
| |
|
Support and Restraint
Selection Factors
• Weight load
• Available
attachment clearance
• Availability of structural
steel
• Direction of loads and/or movement
• Design temperature
• Vertical thermal movement
at supports |
|
| |
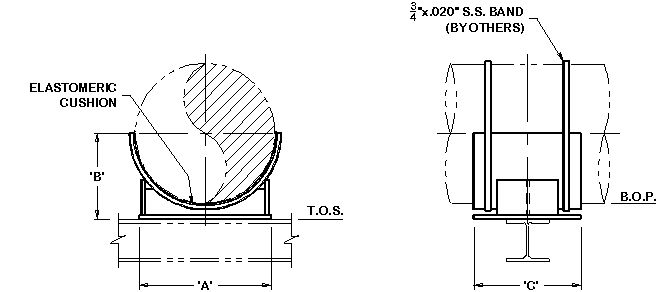
Rigid Supports
Shoe Saddle Base Adjustable
Support
Dummy Support Trunnion |
 |
| Flexible Supports |
|
| |
|
Load and Deflection
Scale
Typical Variable-Load
Spring Support
Small Change in
Effective Lever Arm
Large Change in
Effective Lever Arm
Relatively
Constant
Load
Typical Constant-Load
Spring Support Mechanism |
|
| |
|
Restraints
• Control, limit, redirect thermal movement
– Reduce thermal stress
– Reduce loads on equipment connections
• Absorb imposed loads
–Wind
– Earthquake
– Slug flow
– Water hammer
– Flow induced-vibration
• Restraint Selection
– Direction of pipe movement
– Location of restraint point
– Magnitude of load |
|
| |
|
Anchors and Guides
•Anchor
– Full
fixation
– Permits very limited (if any) translation
or
rotation
•Guide
– Permits movement along
pipe axis
– Prevents lateral movement
–
May permit pipe rotation |
|
| |
|
Piping Flexibility
• Inadequate flexibility
– Leaky flanges
– Fatigue failure
–
Excessive maintenance
– Operations problems
– Damaged equipment
• System must accommodate
thermal
movement |
|
| |
|
| Allowable Pipe Span
Chart |
|
| |
|

