|
INDUSTRIAL VENTILATION DUST COLLECTION SYSTEM DESIGN
HOOD DESIGN
Proper design of exhaust hoods is a must If you want effectively
control athmospheric contanimation at its source with minumum
air flow and power consumption.The theory of capture velocity
depends on the creation of air flow past the source of contaminant
sufficent to remove highly contaminated air around the source
and to draw air into an exhaust hood.
Dust particles in micron sizes ,even if throwed high velocities
travel very short distance and after a few inches follow the iar
currents.The same for mist ,fumes ,vapors and gases.
Larger dust particles relased at high velocities have a trajectory
in air.Unless they are directed to hood ,they cannot be captured..
| |
| Capture Velocity |
V |
fpm |
Air velocity at any point in
front of the hood or at the hood opening ,neccesary to capture
the contaminated air at that poinby causing it to flow into
the hood. |
| |
|
|
|
| Face Velocity |
Vf |
fpm |
Air velocity at the hood opening |
| |
|
|
|
| Slot Velocity |
Vs |
fpm |
Air velocity through the openings in a slot
type hood |
| |
|
|
|
| Plenum Velocity |
Vp |
fpm |
Air velocity in the plenum |
| |
|
|
|
| Duct Velocity |
Vd |
fpm |
Air velocity through the duct after hood. |
| |
|
|
|
| Transport Velocity |
Vt |
fpm |
Minumum air velocity through the duct required
to move particules in air stream. |
| |
|
|
|
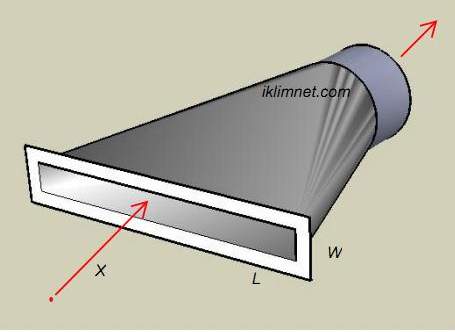
| Dust Distance |
X |
ft |
Distance outward along center axes of hood. |
| |
|
|
|
| Air Flow |
Q |
cfm |
Required minumum air flow to capture dust
particles |
| |
|
|
|
| Area |
A |
ft2 |
Area of hood opening |
| |
|
|
|
| Diameter |
D |
ft |
Diameter of round hoods |
| Hood Design
Procedure |
| |
|
Elimination
of air motion ,important soruce of air motion : |
1 |
Thermal air currents
,especially from hot processes |
2 |
Motion of machinery ,as
grinding wheel ,belt conveyor |
3 |
Materila motion ,as dumping
or container filling |
4 |
Movements of operator |
5 |
Room air currents ,usually
50 fpm ,0,25 m/sn or higher |
6 |
Spot cooling ,heating
equipment |
| |
|
| |
Other considerations |
7 |
The shape of hood |
| 8 |
The size of hood |
9 |
Hood must enclose the
operation as much as possible |
10 |
Location of hood; must
be as close as possible to source |
11 |
Rate of air flow |
12 |
Hood must be flanged
whenever possible to eliminate exhauts air from ineffecitve
areas |
Range
of Capture Velocities in Hood Design
Dust Explosions
A dust explosion is very similar to a gas or vapour cloud explosion,
i.e. when a volume of a flammable mixture is ignited, resulting
in a rapid pressure increase and fire moving through the cloud.
A dust explosion occurs when a combustible material is dispersed
in the air forming a flammable cloud and a flame propagates through
it. This of course also depends on the supply of oxygen to the
fire, and the concentration of the fuel, if either of these are
in too high or low then the explosion will not occur.
|

